What are Brainwaves?
Our brain is an intricate and fascinating organ, with neurons constantly communicating through synchronized electrical impulses. These impulses form what we call brainwaves. Understanding how brainwaves function is key to exploring the workings of both the conscious and subconscious mind. With this knowledge, we can better understand our mental states and how they affect our well-being.
Brainwaves are divided into distinct frequency bands, each associated with different states of consciousness. Think of these waves like musical notes: slower waves resemble the deep tones of a bass drum, while faster ones are like high-pitched guitar notes. Just like in a band, our brainwaves must stay in harmony. If they’re out of sync, we experience mental noise—stress, confusion, or even anxiety.
Our brainwave patterns are affected by what we’re doing and feeling. For example, slower brainwaves dominate when we’re tired or daydreaming, while faster waves are present when we’re alert and focused. Understanding this spectrum of brainwave activity helps us comprehend how our mental states are shaped.
The Five Types of Brainwaves
We typically experience five types of brainwaves, ranging from slow to fast. These brainwaves are measured in Hertz (Hz), or cycles per second, with each frequency representing a different state of consciousness.
1. Delta waves (.5 to 3 Hz)
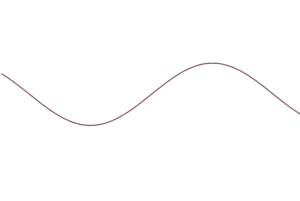
2. Theta waves (3 to 8 Hz)
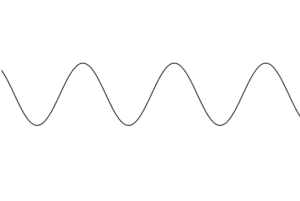
4. Alpha waves (8 to 12 Hz)
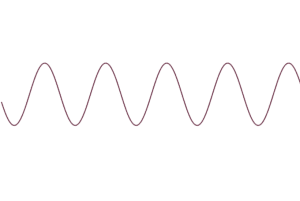
4. Beta waves (12 to 38 Hz)
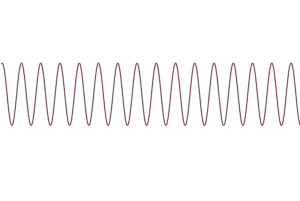
5. Gamma waves (38 to 42 Hz)
How to Influence and Balance Brainwaves
Various techniques have been developed throughout human history to modulate brainwave patterns. Ancient practices such as drumming, chanting, dancing, yoga, and meditation have been used for centuries to alter mental states and bring the mind into balance. In modern times, bi-neural beats and neurofeedback technology also offer ways to regulate brainwave activity.
However, one of the simplest and most accessible methods for balancing brainwaves is through breath control and meditation. Here’s a basic exercise to help calm your mind and promote balanced brainwaves:
- Find a Comfortable Position: Sit cross-legged on the floor or in a chair with a straight back. Place your hands in a relaxed position.
- Focus on Your Breath: Begin by taking deep, regular breaths. As you inhale, think “Calm,” and as you exhale, think “Let go.”
- Stay Present: If your mind wanders, gently bring your attention back to your breathing. Continue this rhythm of deep, regular breathing.
- Relax: Allow your breath to flow naturally, like the tide coming in and out. With time, you’ll notice that simply sitting and breathing brings a sense of peace and joy.
Over time, this practice can help train your brainwaves to move toward balance. When your mind feels overly active, likely dominated by Beta waves, take a moment to slow down and breathe. With consistent practice, you’ll be able to shift your mental state and bring yourself back to calm more easily.
Conclusion
Understanding brainwaves and their impact on our mental states is essential for personal growth and well-being. By incorporating practices such as meditation and breathwork, we can influence our brainwave activity, fostering a healthier balance between relaxation and alertness. The more we tune in to our mental states, the better we can manage stress, improve focus, and cultivate inner peace.


